- ホーム
- Bookkeeping
- Salvage Value A Complete Guide for Businesses
Salvage Value A Complete Guide for Businesses
2022年10月12日
Liquidation value does not include intangible assets such as a company’s intellectual property, goodwill, and brand recognition. However, if a company is sold rather than liquidated, both the liquidation value and intangible assets determine the company’s going-concern value. Value investors look at the difference between a company’s market capitalization and its going-concern value to determine whether the company’s stock is currently a good buy. While you might be able to get your insurer to increase the salvage value of your car, it likely won’t be enough to cover a new vehicle purchase. Depending on your state laws, you might be able to buy back the damaged car from the insurance company.
Free Financial Modeling Lessons
When this happens, a loss will eventually be recorded when the assets are eventually dispositioned at the end of their useful lives. Auditors should examine salvage value levels as part of their year-end audit procedures relating to fixed salvage value assets, to see if they are reasonable. Understanding salvage value helps businesses forecast future cash flows and assess the viability of capital investments. With this knowledge, organizations can optimize resource allocation and enhance their financial strategies. The insurance company decided that it would be most cost-beneficial to pay just under what would be the salvage value of the car instead of fixing it outright. Additionally, consider the example of a business owner whose desk has a useful life of seven years.
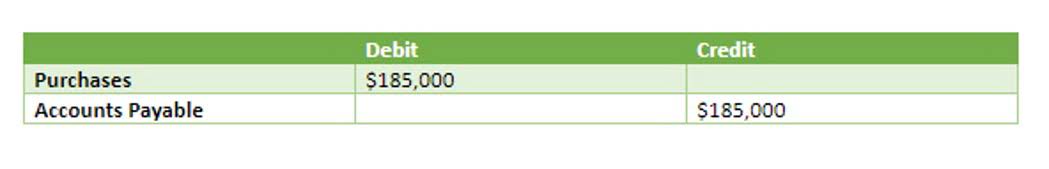
- Regardless of the method used, the first step to calculating depreciation is subtracting an asset’s salvage value from its initial cost.
- The majority of companies assume the residual value of an asset at the end of its useful life is zero, which maximizes the depreciation expense (and tax benefits).
- If a company is still determining how long something will be useful, they might guess a shorter time and say it’s worth more at the end (higher salvage value) to keep it on their books longer.
- It can be calculated if we can determine the depreciation rate and the useful life.
- Other times, it’s about figuring out how much it’s worth when it’s done for good, minus the cost of getting rid of it.
- And the depreciation rate on which they will depreciate the asset would be 20%.
How to Calculate Salvage Value?
There are six years remaining in the car’s total useful life, thus the estimated price of the car should be around $60,000. Each year, the depreciation expense is $10,000 and four years have passed, so the accumulated depreciation to date is $40,000. If the residual value assumption is set as zero, then the depreciation expense each year will be higher, and the tax benefits from depreciation will be fully maximized. The company pays $250,000 for eight commuter vans it will use to deliver goods across town. If the company estimates that the entire fleet would be worthless at the end of its useful life, the salvage value would be $0, and the company would depreciate the full $250,000. It just needs to prospectively change the estimated amount to book to depreciate each month.
Debt Refinancing: Principles, Types, and Financial Impacts

Some companies may choose to always depreciate an asset to $0 because its salvage value is so minimal. Salvage value is the estimated book value of an asset after depreciation is complete, based on what a company expects to receive in exchange for the asset at the end of its useful life. As such, an asset’s estimated salvage value is an important component in https://www.bookstime.com/ the calculation of a depreciation schedule.
Related AccountingTools Courses
Salvage value influences financial statements beyond depreciation calculations, affecting a company’s balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. On the balance sheet, the salvage value contributes to the net book value of an asset, representing the asset’s recorded value after accounting for accumulated depreciation. This figure is pivotal for stakeholders assessing the company’s asset base and its potential for generating future economic benefits. Salvage value is the estimated value of an asset at the end of its useful life. It represents the amount that a company could sell the asset for after it has been fully depreciated.
- Companies can also use industry data or compare with similar existing assets to estimate salvage value.
- The salvage value in a buyback situation is the car’s worth in the condition it is in with the damages it sustained in the accident.
- Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory.
- A car with a salvage title or rebuilt title can be worth thousands of dollars less than a comparable car with a clean title.
- Now, you are ready to record a depreciation journal entry towards the end of the accounting period.
Companies often implement comprehensive maintenance schedules to preserve asset value. We have been given the asset’s original price in this example, i.e., $1 million. The asset’s useful life is also given, i.e., 20 years, and the depreciation rate is also provided, i.e., 20%. After ten years, no one knows what a piece of equipment or machinery would cost. Salvage value or Scrap Value is the estimated value of an asset after its useful life is over and, therefore, cannot be used for its original purpose.

Both declining balance and DDB methods need the company to set an initial salvage value. In such cases, the insurance company decides if they should write off a damaged car considering it a complete loss, or furnishing an amount required for repairing the damaged parts. So, in such a case, the insurance company finally decides to pay for the salvage value of the vehicle rather than fixing it. Salvage value is a critical concept in accounting and financial planning, representing the estimated residual value of an asset adjusting entries at the end of its useful life. When an asset or a good is sold off, its selling price is the salvage value if tax is not deducted then this is called the before tax salvage value.
What Are Operating Costs?
Salvage value is a foundational component in calculating depreciation, determining how an asset’s cost is allocated over its useful life. Depreciation methods, such as straight-line or declining balance, require the initial cost of the asset and its salvage value to calculate the periodic depreciation expense. By subtracting the salvage value from the initial asset cost, businesses derive the depreciable base, which is then systematically expensed over the asset’s lifespan. This approach ensures that the asset’s cost is matched with the revenue it helps generate, adhering to the matching principle in accounting.

- This figure is essential for calculating depreciation and making informed investment decisions, impacting both short-term budgeting and long-term strategic planning.
- This valuation is determined by many factors, including the asset’s age, condition, rarity, obsolescence, wear and tear, and market demand.
- Companies may use software tools like Sage Fixed Assets or Asset Panda to aid in calculating salvage value.
- It equals total depreciation ($45,000) divided by useful life (15 years), or $3,000 per year.
- Residual value and resale value are two terms that are often used when discussing car-purchasing and leasing terms.
- So, if you want to calculate the salvage value of a car, start by determining how much the car would be worth with a clean title.
That company may have the best sense of data based on their prior use of trucks. Companies can also get an appraisal of the asset by reaching out to an independent, third-party appraiser. This method involves obtaining an independent report of the asset’s value at the end of its useful life. This may also be done by using industry-specific data to estimate the asset’s value.










